Fingerprints, the unique patterns etched on our fingertips, have fascinated humans for centuries. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, fingerprints have proven to be invaluable tools in various fields, from forensic science to security. Understanding the different types of fingerprint patterns is essential for a comprehensive grasp of their significance.
This article will delve into the eight major types of fingerprint patterns, providing insights into their classification, characteristics, and implications. By the end, you will have a solid understanding of what fingerprints are, why they are important, and how they are categorized.
What Is a Fingerprint
A fingerprint is a unique pattern of ridges and valleys formed on the fingertips during fetal development. Each individual’s fingerprints are distinct, making them a reliable means of identification.
Biological and Genetic Basis. The formation of fingerprints is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. While genetics plays a significant role in determining the overall pattern, environmental factors such as pressure and friction during development can also contribute to the unique characteristics of individual fingerprints.

Fingerprint Pattern Classification
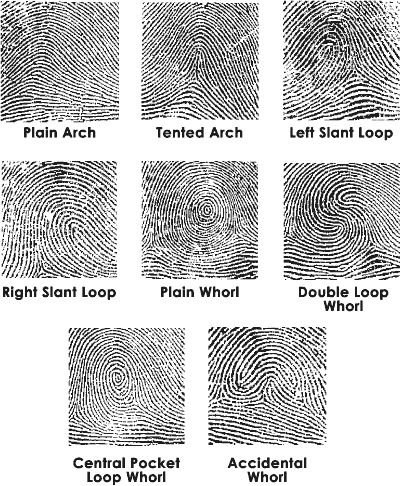
Fingerprint patterns are classified based on their general shapes and characteristics. The most widely used classification system is the Henry-FBI system, which divides fingerprints into eight major types.
The eight major types of fingerprint patterns are:
- Arches.
- Loops.
- Whorls.
The 8 Major Types of Fingerprints
In this section, we will take a detailed look at the eight main types of fingerprints. Each of these types has its own unique characteristics and is classified by the shape of the lines of the papillary pattern. You will learn about types such as arches, loops, and curls, as well as their variations.
Arch Patterns
Plain Arch: This pattern features ridges that flow from one side of the finger to the other, forming a simple arch.
Tented Arch: Similar to the plain arch, but with a sharp, pointed ridge in the center.
Loop Patterns
Ulnar Loop: A loop that flows toward the little finger side (ulnar side) of the hand.
Radial Loop: A loop that flows toward the thumb side (radial side) of the hand.
Whorl Patterns
Plain Whorl: A circular pattern with two or more deltas (triangular-shaped areas).
Central Pocket Whorl: A whorl with a central ridge that does not touch the outer whorl.
Double Loop Whorl: A whorl formed by two intersecting loops.
Accidental Whorl: A pattern that does not fit into any of the other categories.

Fingerprint Patterns and What They Mean
While there is no scientific consensus on the relationship between fingerprint patterns and personality traits, some studies have suggested potential correlations. For example, people with whorl patterns may be more prone to certain personality traits, but these findings are often debated.
It’s important to note that fingerprint patterns are primarily used for identification and have limited implications for personality or other personal characteristics.
Why Are Fingerprint Patterns Important
Fingerprint patterns have been used for identification for centuries, and their importance has only grown with advancements in technology.
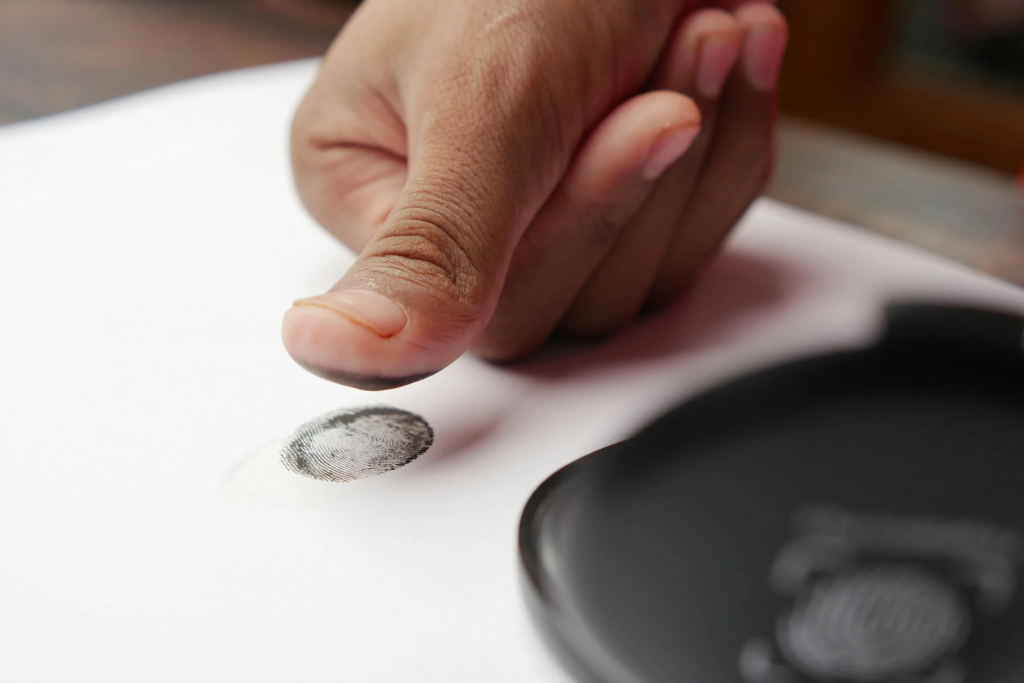
Use in Identification
Fingerprints are considered one of the most reliable methods of personal identification. Law enforcement agencies worldwide rely on fingerprint databases to identify suspects and victims.
Forensic Science
In forensic investigations, fingerprints found at crime scenes can provide crucial evidence linking suspects to the crime. By comparing fingerprints recovered from the scene to known prints, investigators can establish a connection between individuals and the crime.
Biometrics and Security
Fingerprint recognition technology has become increasingly prevalent in modern security systems. Smartphones, access control systems, and even payment methods often incorporate fingerprint scanners to verify identity and prevent unauthorized access.
Trends and Advances in Fingerprint Analysis
Fingerprint analysis has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology leading to more accurate and efficient methods. Digital fingerprinting, for instance, allows for the capture and analysis of fingerprints electronically.
Future trends in fingerprint analysis may include the development of new techniques for enhancing fingerprint quality, improving fingerprint matching algorithms, and integrating fingerprint technology with other biometric modalities.

Fingerprint patterns are a fascinating aspect of human biology, offering a unique means of identification and a glimpse into the intricacies of our genetic makeup. By understanding the eight major types of fingerprint patterns, we gain a deeper appreciation for their significance in forensic science, security, and personal identification.